Ludwig’s Angina
Ludwig’s angina is a severe and potentially life-threatening infection characterized by rapid swelling in the face and neck region.

About Ludwig’s Angina
Dental Health Matters Most
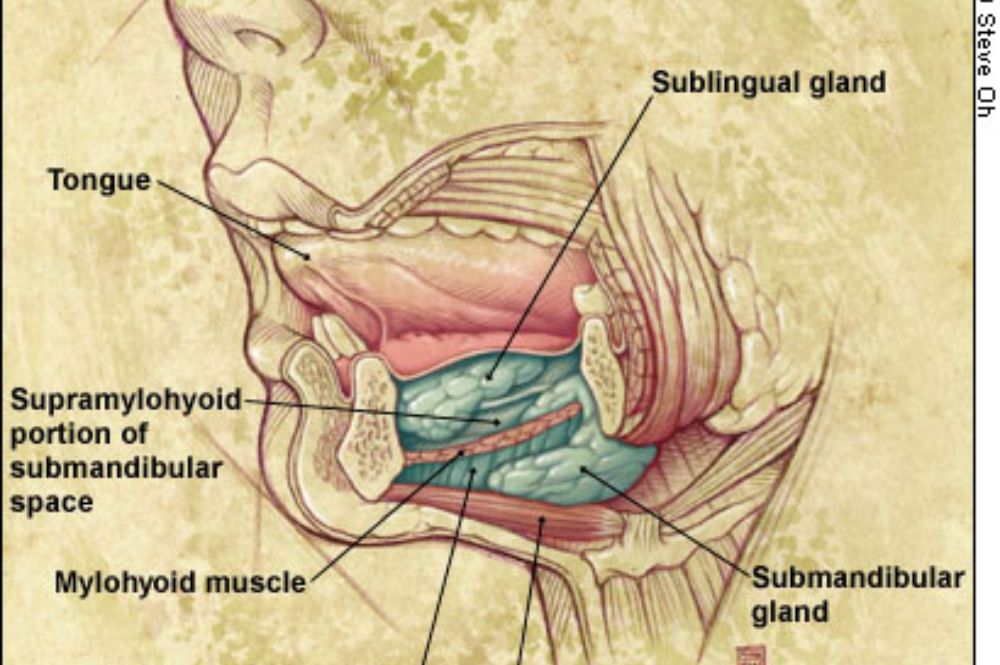
Ludwig’s angina is a severe bacterial infection primarily affecting the floor of the mouth and neck. Often stemming from dental infections, particularly lower molar decay, it spreads rapidly and can obstruct the airway, posing a significant risk. Immediate medical attention is crucial to prevent complications. Treatment typically involves antibiotics, drainage of abscesses, and addressing the underlying dental issues through extraction or other interventions.
Is it Ludwig's Angina?
Determining whether symptoms indicate Ludwig’s angina involves considering facial and neck swelling, rapid onset, and potential airway obstruction. A thorough examination by a healthcare professional, possibly including imaging tests, aids in accurate diagnosis and timely treatment to prevent complications.
How is this possible to occur?
Ludwig’s angina typically arises from a dental infection, particularly involving the mandibular molars, where bacteria spread to the sublingual and submandibular spaces. Polymicrobial flora, including anaerobes and aerobes, contribute to the infection, with immune-compromised individuals being more vulnerable.
Angina in Ludwig and the Dentist? What Connection Do They Have?
Ludwig’s angina and dental issues are closely linked, often stemming from dental decay, infections, or fractures. Various factors such as diabetes, immune deficiencies, and oral cancer can exacerbate the condition, emphasizing the importance of prompt dental care.
How Do We Handle It?
Nirmal Super Specialty Dental Hospital is equipped to handle Ludwig’s angina emergencies with on-site operating rooms and a 24/7 intensive care unit staffed by experienced professionals.
Prompt attention is given to alleviate airway obstructions and administer intravenous antibiotics and pain relief. Surgical interventions, such as incision and drainage, are performed to reduce edema and prevent further spread of infection. Dental extractions are prioritized to eliminate the source of infection and ensure patient recovery.
Advice To Prevent This Deadly Illness
To prevent the onset of Ludwig’s angina, it’s crucial to maintain good oral hygiene by brushing and flossing regularly, attending routine dental check-ups, and promptly treating dental infections or abscesses.
Avoiding tobacco and alcohol consumption can also reduce the risk of oral infections. Additionally, practicing safe oral habits, such as avoiding biting hard objects or using teeth as tools, can help prevent dental trauma that may lead to infections.
Thrombosis in Cavernous Sinus Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis: What Is It?
Cavernous sinus thrombosis is a rare but serious condition characterized by a blood clot forming in the cavernous sinuses, located behind the eyes. This clot can obstruct blood flow from the brain and face, leading to severe complications such as vision loss, paralysis of eye muscles, and potentially fatal infections. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential, typically involving intravenous antibiotics and anticoagulants, along with drainage of any abscesses contributing to the thrombosis.
I Present Myself As Cavernous Sinus Thrombosis And I Look Like This:
Cavernous sinus thrombosis presents with various symptoms, including severe headache, eye pain, vision changes, and facial swelling. Patients may also experience fever, altered mental status, and seizures. The condition often manifests with proptosis, where the eyeball protrudes from the socket, along with paralysis of eye muscles, leading to double vision. These signs indicate a medical emergency, requiring immediate evaluation and treatment to prevent serious complications and preserve vision and neurological function.
Who Bears Responsibility?
Determining responsibility in cases of cavernous sinus thrombosis often involves assessing various factors, including the patient’s medical history, risk factors for thrombosis, and the management of any pre-existing conditions.
Healthcare providers must adhere to best practices in diagnosis and treatment, promptly recognizing symptoms, conducting appropriate investigations, and implementing timely interventions. Failure to recognize and manage risk factors or delays in diagnosis and treatment may lead to adverse outcomes, potentially resulting in legal and ethical ramifications for healthcare professionals involved.
How Are We Going to Handle It?
Handling cavernous sinus thrombosis involves a multidisciplinary approach. Immediate hospitalization and administration of broad-spectrum antibiotics and anticoagulants are crucial to prevent further thrombus propagation and systemic complications. Neurosurgical consultation may be necessary for cases involving intracranial complications. Close monitoring of the patient’s neurological status, along with supportive measures to manage symptoms and prevent complications, is essential. Surgical intervention may be warranted in cases of abscess formation or persistent sepsis despite medical management.
